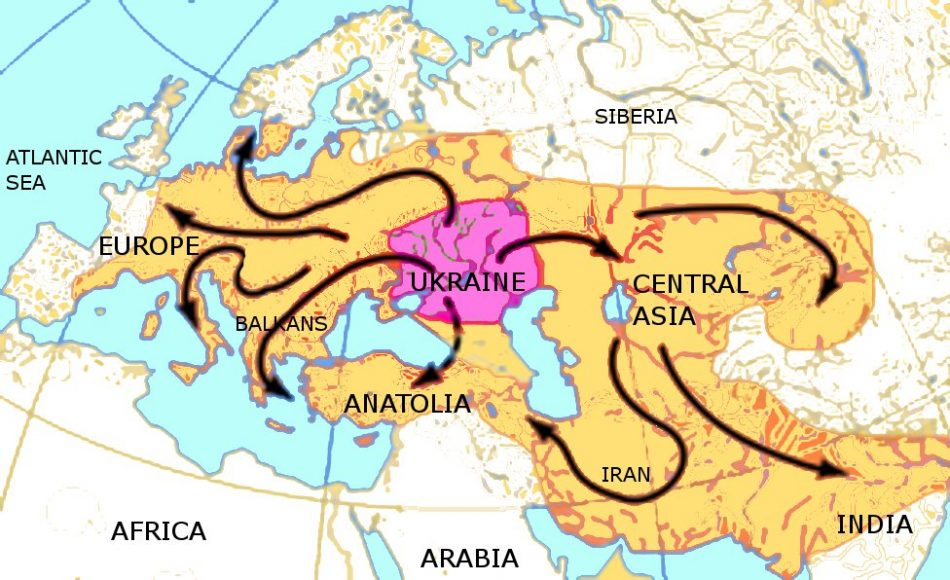
The origins of Indo-European languages have puzzled linguists and historians for centuries, linking more than 400 languages spoken by over 40% of the global population. Recent landmark studies shed light on the Caucasus Lower Volga people, who lived in today’s Russia around 6,500 years ago and are believed to be the speakers of this ancestor tongue. These findings illuminate the genetic ancestry of language, revealing a blend of cultures influenced by the Yamnaya culture, whose nomadic herding practices contributed significantly to the expansion of proto-Indo-European speech. Through rigorous linguistic studies and DNA analysis, researchers have finally pieced together the map of expansion that these languages underwent, tracing their roots back to this ancient populace. Such discoveries not only enhance our understanding of language evolution but also provide critical insights into the socio-cultural frameworks that underpinned early human societies.
Exploring the beginnings of the Indo-European language family invites us to delve into the linguistic roots of many modern tongues, often referred to as proto-Indo-European languages. These ancient languages can be traced back to the Caucasus region and the lower Volga River, where early populations such as the Yamnaya existed. Understanding this linguistic heritage involves examining the intricate tapestry of human interaction, migration, and genetic mixing that occurred over millennia. This journey into linguistic origins is enriched by archaeological findings and advancements in genetic studies that reveal how these early cultures shaped the linguistic landscape we recognize today. As scholars continue to investigate the past, the connections between language and culture become increasingly evident, allowing us to appreciate the profound impact of these ancient societies.
The Origins of Indo-European Languages: A Genetic Perspective
The study of Indo-European languages has taken a monumental leap with recent advances in genetic analysis. Researchers have traced the origins of these languages to the Caucasus Lower Volga region, specifically to populations that lived about 6,500 years ago. This groundbreaking discovery provides insights into how genetic ancestry intersects with linguistic development. Genetic data reveal that the early speakers of Indo-European languages incorporated traits from surrounding groups, leading to a complex tapestry of cultural and linguistic evolution. By integrating findings from linguistic studies and ancient DNA analyses, scientists can now construct a clearer picture of how languages evolved from proto-Indo-European roots.
Furthermore, the implications of this research extend beyond mere linguistic curiosity; they reshape our understanding of ancient migrations and cultural exchanges. The Yamnaya culture, often associated with the spread of these languages, played a crucial role as they migrated across vast distances from the steppes of Russia to various parts of Europe and Asia. This diffusion not only facilitated language spread but also pivotal agricultural and technological advances, illustrating how linguistic journeys are often paralleled by significant cultural transformations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the origins of the Indo-European languages based on recent studies?
Recent studies suggest that the origins of Indo-European languages can be traced back to the Caucasus Lower Volga people, who lived in present-day Russia approximately 6,500 years ago. These individuals were linked to the Yamnaya culture, which played a significant role in the dissemination of proto-Indo-European languages across Europe and into Asia.
How does genetic ancestry relate to the origins of Indo-European languages?
Genetic ancestry studies indicate that the Caucasus Lower Volga people, who are considered the originators of the Indo-European language family, mixed with various local populations. This genetic interaction facilitated the spread of their languages, revealing a complex migration pattern that influenced the linguistic landscape of Europe and South Asia.
What role did the Yamnaya culture play in the development of Indo-European languages?
The Yamnaya culture was crucial in the development of Indo-European languages as they are believed to be among the first speakers of proto-Indo-European tongues. Their nomadic pastoralist lifestyle allowed them to spread their language and culture across vast distances, significantly impacting the linguistic evolution in regions spanning from Europe to the Indian subcontinent.
What evidence supports the connection between the proto-Indo-European language and the Caucasus Lower Volga people?
Evidence from archaeological findings, DNA studies, and linguistic reconstructions indicates that the Caucasus Lower Volga people were the earliest known speakers of proto-Indo-European languages. Their interactions with adjacent cultures and incorporation of various biological and linguistic elements substantiate their role as pivotal figures in the origins of Indo-European languages.
How do linguistic studies inform our understanding of the origins of Indo-European languages?
Linguistic studies have played a vital role in tracing the origins of Indo-European languages by identifying similarities between languages such as Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit. These studies, combined with archaeological and genetic data from the Caucasus Lower Volga and Yamnaya cultures, provide a comprehensive understanding of how these languages evolved and spread across different regions.
| Key Points | Information |
|---|---|
| Origin of Indo-European Languages | Indo-European languages originated from new research identifying the Caucasus Lower Volga people in what is now Russia, approximately 6,500 years ago. |
| Research Significance | The findings provide genetic links to the Yamnaya people who were thought to have carried these languages across Europe and beyond. |
| Methodology | The research utilized ancient DNA analysis from 354 individuals across various archaeological sites. |
| Cultural Impact | The study also discussed the Yamnaya culture’s demographic explosion and their burial practices, which helped researchers understand their origins. |
| Broader Implications | These discoveries link population migrations from the Caucasus Lower Volga region to the language dispersion across Europe and parts of Asia. |
Summary
The origin of Indo-European languages has been a topic of intense research, leading to groundbreaking discoveries that trace back to the Caucasus Lower Volga people. This research highlights a significant demographic and linguistic expansion that occurred around 6,500 years ago, profoundly influencing the linguistic landscape we see today. By understanding the roots of these languages and the migrations of their speakers, we gain valuable insight into early human cultures and their connections.