Brain-Computer Interfaces: Promise and Peril of Technology
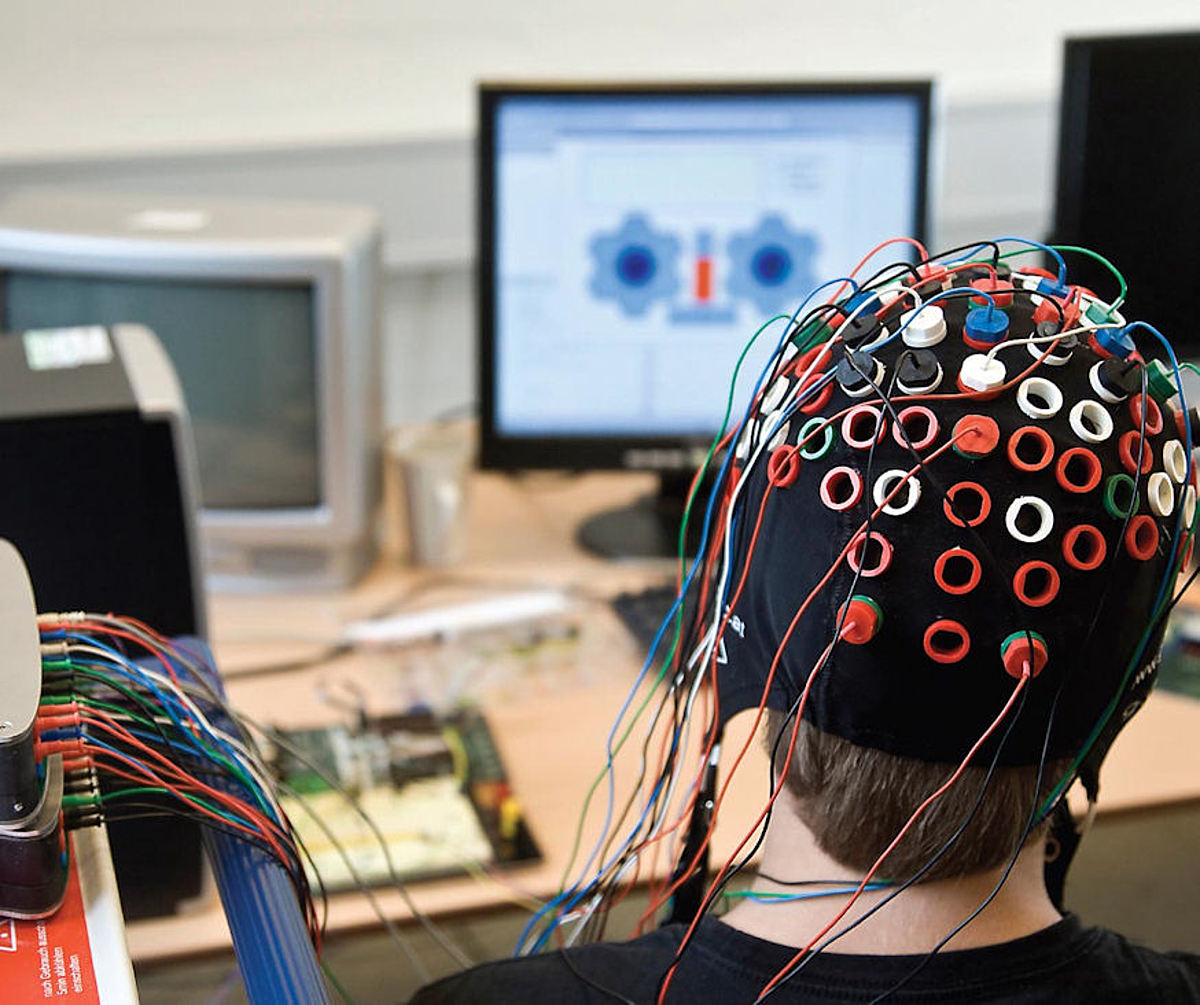
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are revolutionizing the way we interact with technology and understand the human brain. These advanced neural devices, such as those developed by Neuralink, are designed to create direct communication pathways between the brain and external devices, holding potential for incredible applications. From helping individuals with disabilities control prosthetic limbs to enabling thought-based computer operation, BCI technology opens up a new world of possibilities. The emergence of brain chip implants raises exciting yet complex ethical questions and sparks discussions about mind control and neurotechnology’s implications. As scientists and researchers dive deeper into this groundbreaking field, the future of human augmentation and cognitive enhancement seems closer than ever before.
The concept of direct brain-machine communication is at the forefront of modern neurotechnological advancements. Often referred to as neural interfaces or thought-control devices, these innovative technologies aim to bridge the gap between human cognition and digital interaction. Through the use of sophisticated implants, researchers explore the potential of enhancing cognitive functions, controlling devices merely through thought, and addressing neurological disorders. This new wave of neuroengineering is transforming our understanding of the brain’s capabilities and how we can utilize its power in unprecedented ways. As these technologies progress, they bring forth both transformative possibilities and ethical responsibilities that society must carefully navigate.
Understanding Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs)
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) represent a revolutionary technology that bridges the gap between human cognition and machine functionality. These neurotechnological devices allow individuals, particularly those with physical disabilities, to control computers or prosthetic limbs through their brain signals. By bypassing traditional motor pathways, BCIs can decode neural activity and translate it into actions, thereby enabling users to interact with devices purely through thought. This has profound implications for rehabilitation, as it empowers users to regain agency over their movements and interactions with the world.
The potential market for BCIs is vast, projected to reach approximately $400 billion in the United States alone. This staggering figure highlights the urgent need for ethical considerations as the technology develops. As companies like Neuralink advance their offerings, understanding the implications of such technologies on mental privacy and autonomy becomes crucial. There is an increasing concern about the dual-edged nature of BCI advancements, which promise significant benefits but also harbor the potential for misuse in the realms of mind control and ethical violations.
The Implications of Neuralink and BCI Technologies
Neuralink, spearheaded by Elon Musk, has garnered significant attention for its pioneering work in BCI technology. The company’s recent success in implanting a brain chip in a paralyzed patient demonstrates the incredible capabilities of neurotechnology to improve quality of life significantly. The ability for individuals to control a computer mouse or engage in activities like playing online chess merely by thought is a testament to the technology’s promise. However, as with any groundbreaking advancement, there are ethical considerations and historical precedents that warrant cautious optimism.
As Lukas Meier’s discussions highlight, the possibilities inherent in BCI technology extend beyond enhancing abilities; they also usher in concerns regarding consent, mental privacy, and potential exploitation. The historical context of mind control experiments conducted during the Cold War serves as a stark reminder of how technology can be weaponized, leading to severe ethical breaches. The challenge lies in balancing the positive impacts of neurotechnology, such as improving lives through rehabilitation, while safeguarding against its potential use for manipulation or control.
Historical Context: Mind Control and Ethical Dilemmas
The dark history of mind control experiments, particularly during the Cold War era, raises pertinent questions about the use of modern neurotechnologies like BCIs. Programs such as the CIA’s MKUltra sought to manipulate human behavior and consciousness through coercive means, often with devastating effects on subjects. As we navigate the landscape of contemporary BCI technology, it’s essential to heed the lessons from this past. Recognizing the ethical implications of using advanced neurotechnologies to manipulate thoughts or behaviors is paramount.
Today, the landscape looks quite different, yet similar ethical dilemmas persist. The potential for BCIs to be misused continues to loom large. Historical cases illustrate how desires for control can lead to significant human rights violations and suffering. As we push forward into this new frontier of technology, ensuring transparency and ethical oversight will be crucial in preventing history from repeating itself in the realm of neurotechnology.
Neurotechnology: Opportunities vs. Risks
Neurotechnology, particularly through advances in brain-computer interfaces, presents a unique mixture of opportunities and risks. On one hand, BCIs hold incredible potential to transform the lives of those with disabilities, providing pathways to communicate and interact that were previously impossible. Individuals with paralysis can regain some autonomy and participate more fully in society as they gain the ability to control devices through brain activity. This innovation undoubtedly paints a hopeful picture for the future of rehabilitation and assistive technology.
However, the dark shadows of past misuse linger, creating a chilling undercurrent to the excitement surrounding BCIs. Concerns about self-determination, mental privacy, and the potential for neurotechnology to facilitate unethical behaviors call for a careful examination of how these technologies are developed and implemented. As society embraces these advancements, it is essential to establish rigorous safeguards to ensure that the risks do not outweigh the benefits, thus maintaining the integrity of individual autonomy.
Navigating Ethical Concerns in BCI Development
As BCI technology evolves, ethical considerations must take center stage. The promise of devices that can decode thoughts or manipulate behaviors presents unprecedented questions regarding consent and mental privacy. Developers must grapple not only with the technical challenges of creating effective BCIs but also with the moral implications of their applications. In navigating this landscape, it is crucial for researchers and companies to adopt ethical frameworks that prioritize user rights and autonomy.
Moreover, discussions surrounding informed consent become increasingly complex as neurotechnologies advance. Individuals may not fully comprehend the implications of utilizing BCIs, particularly regarding their mental privacy and potential vulnerabilities. Establishing clear guidelines and educational resources for users can help mitigate risks and empower individuals to make informed decisions about their involvement with these technologies, ensuring that progress does not come at the expense of personal freedoms.
Future Directions for Brain-Computer Interface Technologies
The future of brain-computer interface technologies is ripe with potential breakthroughs that could redefine human interaction with machines. As research expands and more patients like Noland Arbaugh receive implants, the data collected will undoubtedly enhance our understanding of brain functions and responses. This advancement could pave the way for novel applications, ranging from advanced clinical therapies for neurological disorders to new forms of human-computer interaction that transcend traditional boundaries.
However, the innovation landscape is not without challenges. As capabilities increase, so too do the risks associated with misuse. Regulatory frameworks must evolve concurrently to monitor and guide the development of BCI technologies, ensuring that they are used responsibly and ethically. The collective journey forward will involve not just technical feats but also an ongoing dialogue around the ethical implications of integrating these devices into everyday lives.
Regulatory Framework and Public Perception of BCIs
As BCIs continue to evolve, establishing a robust regulatory framework will be essential for maximizing their benefits while minimizing potential harms. Government bodies, alongside researchers and ethical committees, must collaborate to create safe guidelines that address the multifaceted challenges posed by BCIs. These regulations will need to ensure that users are protected from exploitation and that their mental privacy is upheld in the face of advancing technologies.
Public perception also plays a crucial role in the acceptance and implementation of BCI technologies. Misunderstandings or fears surrounding mind control and manipulation can hinder progress and widespread use. Engaging in informative discussions that clarify the science and ethical considerations surrounding BCIs is essential. By fostering an environment of openness, innovation can thrive while addressing societal concerns about privacy and autonomy.
The Role of Stakeholders in BCI Development
As brain-computer interfaces redefine human capability and interaction, it is paramount that all stakeholders—researchers, developers, ethicists, and the public—actively participate in their development. Diverse perspectives can facilitate comprehensive approaches to creating BCIs that not only focus on technical advancement but also prioritize ethical standards and user welfare. Emphasizing collaboration among stakeholders can yield better outcomes for patients and society as a whole.
With the potential for BCIs to impact lives profoundly, it is critical that stakeholders advocate for responsible research practices and transparent communication. Encouraging interdisciplinary collaboration can help to identify potential pitfalls and address them proactively. Engaging the public in ongoing dialogues about the implications and expectations surrounding BCI technology will foster a more informed and receptive environment for future developments.
Ensuring Safe Integration of Neurotechnology in Society
As brain-computer interface technology becomes more integrated into everyday life, the paramount concern must be the safety of users and the ethical implications of its use. Efforts to ensure that BCIs can coexist harmoniously with societal norms and values are crucial. This includes continuous monitoring of the effects of implant technology, as well as enforcing rigorous consent processes that can adapt to changing technology and public sentiment.
Promoting an ethical framework for the integration of neurotechnology requires proactive measures from all involved parties. It is essential to establish an environment where users feel secure and informed about the capabilities and limitations of BCIs. Ultimately, prioritizing safety not only enhances user trust but also helps ensure that these groundbreaking advancements truly serve humanity without infringing on individual rights.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are brain-computer interfaces and how do they work?
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are advanced neurotechnology systems that allow direct communication between the brain and external devices. They work by interpreting brain signals and translating them into commands for computers or prosthetics, enabling individuals to control devices with their thoughts. BCIs hold potential for helping people with disabilities perform tasks independently.
How does Neuralink utilize BCI technology?
Neuralink is a pioneering neurotechnology company that develops brain-computer interfaces designed to connect human brains directly to computers. By implanting brain chip devices, Neuralink aims to restore functionalities for individuals with spinal cord injuries and neurological disorders, enabling them to interact with technology via thought, such as controlling a computer mouse or participating in online games.
What are the potential applications of brain chip implants?
Brain chip implants, part of BCI technology, have numerous potential applications, including assisting individuals with paralysis in controlling prosthetic limbs, allowing people to communicate through thought, and improving therapeutic outcomes for neurological conditions. These devices could revolutionize how we interact with technology and enhance quality of life.
What are the ethical concerns surrounding mind control and BCIs?
The advancement of brain-computer interfaces raises significant ethical concerns, particularly regarding mind control and mental privacy. Historical precedents, such as MKUltra, highlight the potential misuse of neurotechnology for manipulating behavior or extracting information from individuals against their will. Therefore, the development of BCIs necessitates careful consideration of consent and rights.
Can BCIs decode thoughts and influence behavior?
Research indicates that brain-computer interfaces can decode certain thoughts and intentions based on brain activity. There are also concerns that BCIs could inadvertently influence behavior. Instances such as patients exhibiting uncharacteristic actions while receiving deep brain stimulation illustrate the complex relationship between BCI technology and behavioral control.
What is the market potential for BCI technology?
The market for brain-computer interfaces is projected to reach approximately $400 billion in the U.S. alone, driven by the increasing prevalence of spinal cord injuries, strokes, and neurological disorders. As technology advances and applications expand, the demand for innovative BCI solutions is likely to grow significantly.
How do brain-computer interfaces differ from traditional assistive technologies?
Unlike traditional assistive technologies that rely on physical interfaces (like switches or joysticks), brain-computer interfaces provide a direct link between the brain and external devices. This allows for more intuitive control and interaction, making them especially beneficial for individuals with severe physical limitations, as they can operate devices purely with their thoughts.
What risks are associated with brain chip implants?
Brain chip implants carry various risks, including surgical complications, potential for infection, and ethical concerns around privacy and consent. Additionally, the long-term effects of neural implants on mental health and behavior are still being studied, necessitating ongoing research and regulatory scrutiny.
How can we ensure ethical development of BCI technology?
To ensure the ethical development of brain-computer interface technology, it is essential to establish robust guidelines that prioritize user consent, mental privacy, and safety. Ongoing dialogue among technologists, ethicists, and regulatory bodies is crucial to address potential risks and ensure that BCIs are used for beneficial purposes without infringing on individual rights.
What role do BCIs play in the future of neurotechnology?
BCIs represent a significant advancement in neurotechnology, offering transformative potential for medical therapies, rehabilitation, and enhancing human-computer interaction. As research and innovation continue, BCIs may redefine how we interact with technology, promote independence for individuals with disabilities, and even open new frontiers in human cognition.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Introduction to BCIs | Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are devices that allow individuals to control computers or prosthetic limbs directly with their thoughts, showing potential therapeutic benefits for people with disabilities. |
| Noland Arbaugh’s Case | On January 28, 2024, Noland Arbaugh became the first person to receive a Neuralink brain chip implant, enabling him to control a computer mouse and play chess through thought alone. |
| Market Potential | With millions of spinal cord injury and stroke cases, the BCI market is expected to reach approximately $400 billion in the U.S. |
| Historical Context | A discussion paper compares the development of BCIs to past psychological manipulation efforts, warning of potential abuses of the technology. |
| Risks of Mind Control | The author, Lukas Meier, warns that BCIs might enable forms of behavior control reminiscent of Cold War-era mind control experiments. |
| Concerns for Ethics | The use of BCIs raises ethical issues regarding consent, self-determination, and mental privacy, particularly with advances in brainwave tracking. |
| Support for Development | Meier advocates for the continued development of BCI technology in the U.S. to prevent adversaries from gaining an advantage in its use. |
| Potential Behavioral Changes | Some BCIs might unintentionally alter behaviors, with instances of patients experiencing manic symptoms from deep brain stimulation. |
Summary
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) represent a significant technological advancement with the potential to transform the lives of individuals with disabilities. However, while the promise of BCIs is substantial, lessons from history caution against unregulated use, as they remind us of the ethical implications surrounding mind control and consent. As we move forward in developing these technologies, it is imperative to weigh their benefits against the potential risks, ensuring that we prioritize the rights and safety of individuals.